Special yeast cell wall for mycotoxin binding

YeaMOS T has the advantages of adsorption sites in the yeast cell wall and possesses excellent adsorption effect in the toxins. In this article you will learn more about this mycotoxin binder.
Mycotoxins are secondary metabolites of moulds that are ubiquitous in feed and feed raw materials. At present, there are about 100 kinds of mycotoxins known to contaminate the feed, mainly a variety of mycotoxins produced by Penicillium, Aspergillus and Fusarium, of which the main hazards to livestock and poultry are aflatoxin, ochratoxin, fumigatus toxin, trichothecene mycotoxin and zearalenone. At least 25% of the world’s cereals are contaminated with mycotoxins, causing serious harm to the feed industry, animal husbandry and human health.
Many researchers have made a lot of research on how to eliminate the adverse effects of mycotoxins on the health and production performance of livestock, reduce the residue of mycotoxins and their metabolites in the final products, and ensure the food safety for humans.
Application of yeast cell wall as mycotoxin adsorbent
Adding mycotoxin adsorbent to feed is an effective means to reduce the harm of mycotoxins and improve the production performance of animals. At present, one of the main components of the mycotoxin adsorbent is the yeast cell wall. Why yeast cell wall has this kind of functions?
So, what is the mechanism of mycotoxin adsorption by yeast cell wall? Studies showed that the yeast cell wall network structure mainly consists of polysaccharides, with the outer layer made of heavily glycosylated mannoproteins involved in cell recognition and the inner layer made of β-1,6- and β-1,3-glucan chains linked with chitin and mannoproteins to give rise to the fibrous network structure.
There are at least three pathways of mycotoxin adsorption by yeast cell wall:
(1) Physical structure and morphology theory. The yeast cell wall with greater thickness and content has a greater mycotoxin detoxification ability. In contrast, the mycotoxin removal percentage dramatically decreased when the yeast cell wall three-dimensional network was artificially damaged;
(2) Chemical components theory. The insoluble β-1,3-glucans provides a large of binding sites by forming a complex branched architecture for ZEN adsorption, which could be enhanced by soluble β-1,6-glucans. A similar collaboration function is observed between β-1,3-glucans, and chitin, those two, as the main structural frame of the yeast cell wall, could provide many meshes for patulin molecule adsorption.
(3) Interaction between structure and components. The recent study revealed that genetic modification technology could regulate the yeast cell wall thickness, chemical composition (such as the ratio of β-1,3- and β-1,6-glucans, and chitin and network formation of reticular structures to achieve an mycotoxin adsorption enhancement.
YeaMOS T, a special yeast cell wall for mycotoxin binding
Angel yeast as the world’s leading yeast cell wall manufacturer and research company, has been developing yeast cell wall products as mycotoxin adsorbents for nearly 30 years. We have established a rapid and efficient in vitro simulation evaluation system, and found that there were significant differences in functional indexes of yeast cell wall products from different sources, as well as the adsorption efficiency of mycotoxins such as zearalenone.
Figure 1- Adsorption rate of different YCW for ZEN in vitro (%; Angel Yeast, 2016).
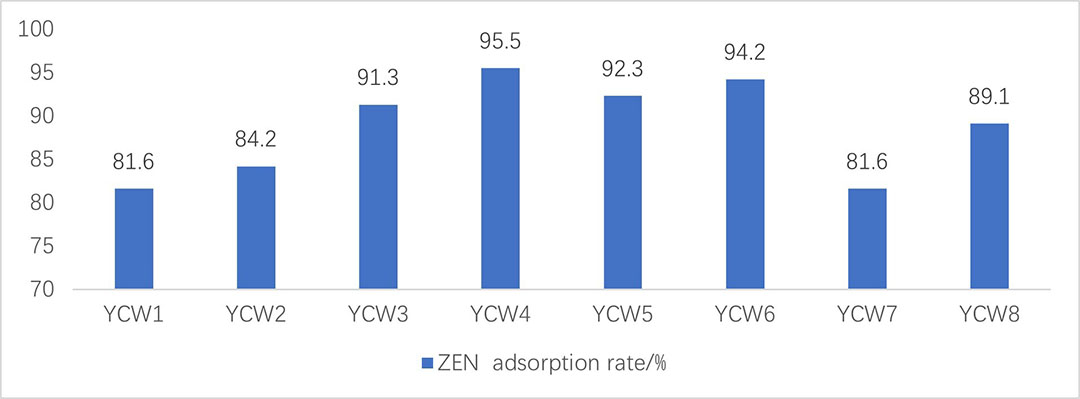
YeaMOS T is an effective broad-spectrum product manufactured by optimum selection of yeast as raw material, adoption of advanced purification technology, special enzymolysis, as well as construction and activation of yeast cell wall. For deep research, we find that the adsorption of mycotoxins by YeaMos T is mainly based on the spatial structure and composition of it, which mainly includes adsorption and degradation as table 1 shows.
Meanwhile, because of the differences of resources as well as deep-processes, the absorption capacity of YeaMOS T compared with some inactive yeast products are totally different as Table 2 shows. Overall, the adsorption effect of pure yeast cell wall products on mycotoxin was better than that of inactive yeast powder, and the special yeast cell wall (YeaMOS T) is the best.
Conclusion
YeaMOS T, which has been strengthened the advantages of adsorption sites in the yeast cell wall and possesses excellent adsorption effect in the toxins. It can be widely used in mycotoxin binders to improve feed safety and effectively protect animal health, as well for the compound mycotoxin binder producers.
References are available on request.






